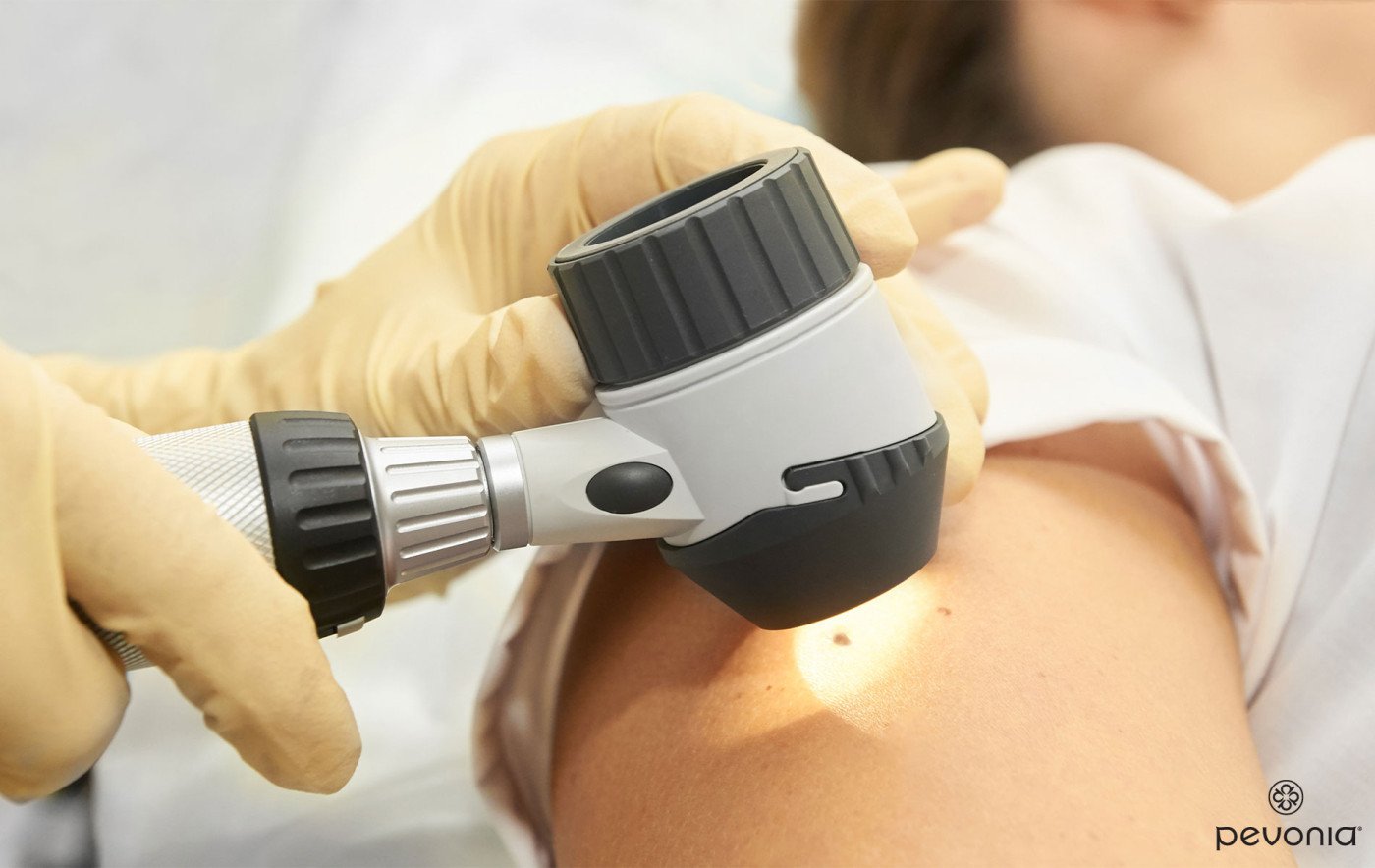
Skin Cancer on The Rise
In the United States, roughly 9,500 people are diagnosed with skin cancer daily, with approximately 5 million people currently being treated for the disease, making skin cancer the most common form of cancer in the U.S. With early detection and treatment, forms like basal and squamous cell carcinoma are highly treatable. But melanoma is more complicated. Reports indicate that the percentage of people with melanoma has doubled over the last three decades!
Who Is Affected
Per the Skin Cancer Foundation, “1 in 5 Americans will develop skin cancer by the age of 70.” However alarming these statistics are, information about the number of new melanoma cases and fatalities can be confusing. And while everyone is vulnerable, melanoma is shown to affect different sexes and age groups at varying rates and degrees.
New Cases: The Melanoma Research Alliance indicates that new melanoma diagnoses have increased by 27% since 2013. According to estimates from the American Cancer Society, approximately 100,640 new melanoma cases are projected for 2024, with approximately 59,170 for men and 41,470 for women. Some sources cite that melanoma is the most diagnosed cancer in individuals aged 25 to 39. In contrast, others show that the rates of new melanoma diagnoses have stabilized in people younger than 50, refuting this alleged overall rise. So, why is melanoma increasing? The risk of melanoma increases as we age, with 65 being the average age of diagnosis. The numbers specifying a rise may be attributed to the burgeoning population of aging baby boomers—a demographic that grew up in an era that prized tanning and had little to no awareness of the effects of UV exposure. However, overdiagnosis is another possible reason for the rising melanoma statistics. Here’s why melanoma is overdiagnosed:
- Specialized training leading pathologists to deem abnormal, nonmalignant tumors that mimic melanoma as early-stage melanomas
- Patient fears and anxiety elevating physician concern about missing potential cancer diagnoses
Fatalities: According to the skin cancer foundation, two people die from skin cancer every hour in the United States. Melanoma is responsible for the deaths of nearly 20 Americans daily, with 8,290 estimated to perish due to this skin cancer annually. Sources suggest that the total death rates for melanoma actually declined from 2013 to 2017 due to skin cancer treatment advances, a decline of roughly 6 - 7% per year. With about 4,430 men and 2,860 women expected to succumb to melanoma in 2024, it appears that men are more affected. Why is melanoma so deadly for men? Men are less inclined to shield their skin from the sun with sunscreen or other face products with SPF, and studies confirm that men's skin is more adversely affected by UV rays than women's. The AAD also suggests that the inherently thicker nature of men's skin, containing more collagen and elastin fibers yet less fat, plays a role. Despite this disparity, women must continue to be vigilant about sun protection. Melanoma is the #1 cause of cancer death for young women ages 25 - 30 and the second biggest cause of cancer death for women 30-35 years old.
Skin Cancer Causes
Excess UV radiation from sunlight and indoor tanning are the prime culprits of skin cancer, coupled with personal history, family history, and genetics. Having parents, siblings, or children with melanoma and being white significantly increases your risk of acquiring the disease. 10% of people with a family history get melanoma, a disease that affects fair-skinned whites 20 times more often than blacks and people with highly pigmented skin. While annual skin cancer screening is vital for everyone, getting checked every three to six months is critical for people with high risk factors.
Why Melanoma Is So Deadly
Did you know just five or more sunburns over your lifetime doubles your melanoma risk? And although tanning beds were “sold” as safe alternatives to direct sun exposure, their usage before age 35 is linked with increasing melanoma risk by 75%. Melanoma is a fast-growing form of skin cancer that can metastasize, spreading to other body parts, which partly explains why it is life-threatening. As it may appear on unexposed skin, it can more easily go undetected and therefore is less likely to be treated in a timely manner. And it isn’t just the skin that is affected. Ocular melanoma, cancer of the eye, also results from exposure to UV-emitting tanning beds and devices.
Skin Cancer Prevention
Avoiding excess UV exposure from sunlight and indoor tanning is imperative to avoid skin cancer. When it isn’t possible to stay out of the sun, applying sunscreen with broad spectrum sun protection every two hours is critical. For optimal skin cancer prevention, adopt other sun protection measures like avoiding peak hours (between 10AM and 4PM), using umbrellas, and wearing wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and UPF clothing. Despite the improvements in skin cancer survival rates, with the growing prevalence of melanoma’s potentially fatal form of cancer, every month should be Skin Cancer Awareness Month!
